ON THIS PAGE
Understanding Adobe Edge Delivery Services (EDS)
Adobe Edge Delivery Services (EDS) is Adobe’s modern content delivery framework for delivering high-performance, content-driven websites. It redefines how web experiences are built, created, and launched by combining headless architecture, quick edge caching, and direct document-based authoring.
In simple terms, EDS connects Adobe Experience Manager (AEM) or Adobe Experience Cloud with an edge network to deliver content instantly, without the heavy server-side rendering and complicated deployments of traditional CMS platforms. It’s built for flexibility. Authors can use familiar tools like Microsoft Word or Google Docs to create content. Developers can code lightweight frontends, and both can work together using a modern GitHub-based workflow.
Common Business Challenges in Modern Web Delivery
Modern businesses face several challenges in delivering high-quality digital experiences:

- Slow website performance: Traditional CMS architectures depend more on backend servers. This will lead to delays and poor user experiences.
- Complex authoring workflows: Marketing teams often find it hard to work with rigid authoring tools. These tools slow down content updates.
- Expensive infrastructure and maintenance: Monolithic systems require regular optimization, scaling, and deployment efforts.
- Inconsistent brand experience: Managing multiple sites or regions often creates scattered content and broken workflows.
- SEO and conversion drops: Slow load times hurt SEO rankings and conversion rates, which affects revenue.
How Adobe Edge Delivery Services Solves These Challenges
EDS solves these challenges with a modern, performance-first approach:
- Edge-first architecture: Content will be served from Adobe’s global CDN edge, reducing latency dramatically.
- Document-based authoring: Authors can use tools like Google Docs or Microsoft Word to create pages — no need to log into complex CMS editors.
- GitHub integration: Every change in content or code is version-controlled, reviewed, and deployed automatically to the nob-prod / prod environments.
- Composable and headless: EDS integrates easily with Adobe Commerce, Adobe Analytics, and AEM for dynamic, personalized experiences.
- Automatic performance optimization: EDS optimizes HTML, images, and scripts during delivery by ensuring very fast Core Web Vitals out of the box.
Key Business and Site Impact of Using EDS
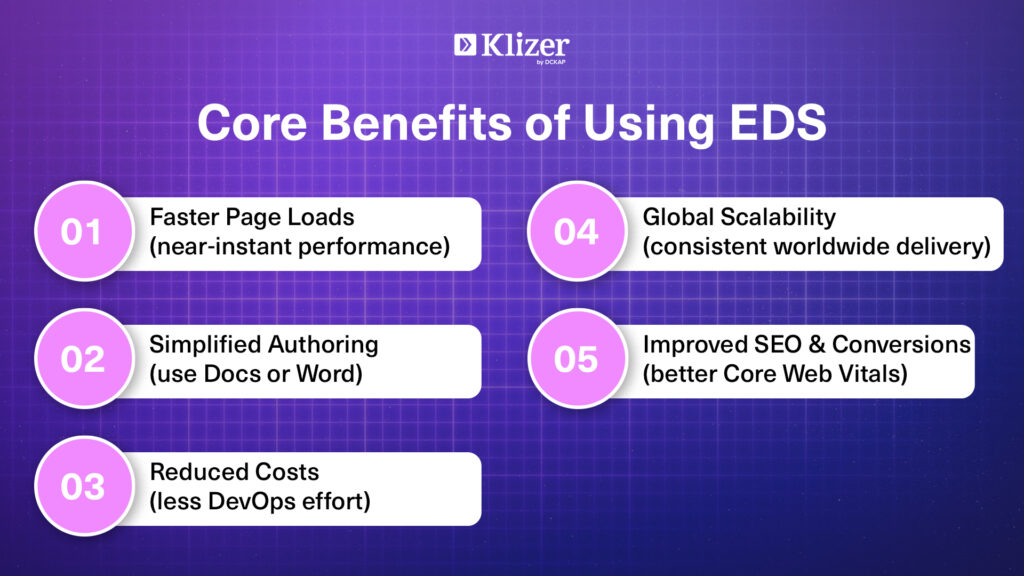
- Faster Page Loads: Websites built on EDS load almost instantly, often scoring almost perfect Core Web Vital scores.
- Simplified Workflow: Marketers can publish content directly from Docs, while developers manage structure and templates in GitHub.
- Reduced Operational Cost: Lightweight architecture and automated deployments minimize DevOps overhead.
Scalable Global Delivery: Adobe’s edge network ensures consistent performance worldwide. - Better Engagement and Conversions: Improved speed and accessibility lead to higher SEO rankings and better customer satisfaction.
Key Benefits of Adobe Edge Delivery Services
The primary focus of EDS is delivering exceptional performance and improving efficiency for both authors and developers.
| Category | Key Benefit | Explanation |
| Performance | 100 Lighthouse Score | EDS is engineered to achieve perfect Google Lighthouse performance scores out-of-the-box, leading to excellent SEO and a better user experience. |
| Faster Load Times | Content is served from the network’s edge, minimizing latency and significantly reducing page load times (often to ~1 second). | |
| Authoring | Document-Based Authoring | Authors use familiar tools like Google Docs or Microsoft Word/SharePoint as the content source, drastically simplifying content creation, editing, and publishing. |
| Fast Time-to-Market | Content updates go live within seconds of publishing from the source document, eliminating complex build/deployment cycles. | |
| Development | Developer Efficiency | Developers work with plain HTML, modern CSS, and vanilla JavaScript, avoiding the complexity of specialized AEM frameworks or heavy configurations. The code is hosted on GitHub. |
| Composable Architecture | It allows you to deliver content headless or headful and easily integrate with other services, offering great flexibility. |
Adobe Edge Delivery Services – Boilerplate Code Setup Guide
Follow the steps below to create and configure your EDS storefront using the boilerplate repository and Adobe tools.
Step 1: Create Your Site Repository
- Start by generating a storefront repository using Adobe’s official boilerplate template: AEM Boilerplate Commerce Template
- This template provides the basic folder structure, configuration files, and sample components required for an EDS storefront.
- Once created, clone the repository locally or open it directly in GitHub for configuration.
- Screenshot:
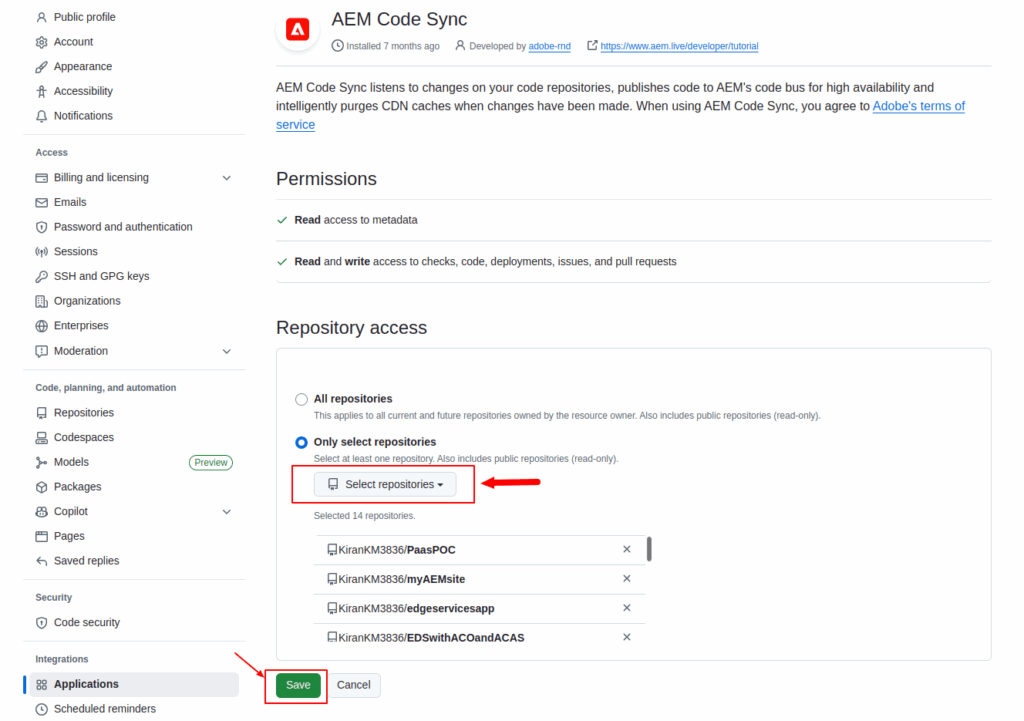
Step 2: Install and Configure the AEM Code Sync App
- Next, install the AEM Code Sync App in your GitHub repository: AEM Code Sync App
- This app plays a key role in your EDS setup:
- It automatically redeploys your storefront when changes are pushed to the main branch.
- It enables Edge Delivery System (Helix Admin) to access your repository, allowing content and code updates to stay synchronized.
- After installation, configure the app to connect to your new GitHub repository. Once linked, the deployment pipeline will be managed automatically, no manual triggers needed.
- Screenshot:
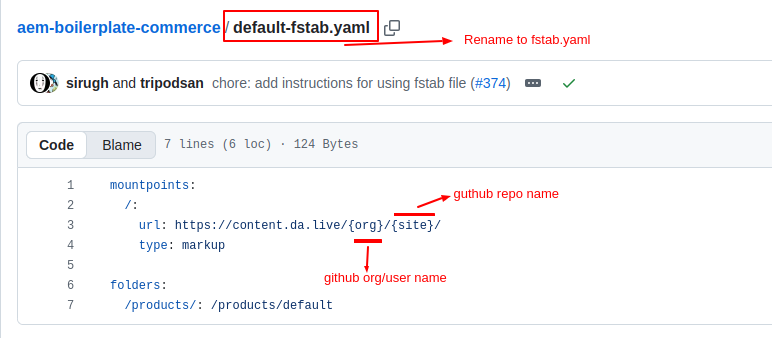
Step 3: Link Repository to Content
Now connect your code repository to your content source using the fstab.yaml file.
- Locate or create a file named fstab.yaml in your repository root.You can use the provided default-fstab.yaml as a reference.
- Rename default-fstab.yaml → fstab.yaml.
- Update the placeholders:
- mountpoints : /: https://<github-org-or-username>.github.io/<reponame>/
- Replace <github-org-or-username> and <reponame> with your actual organization/user name and repository name.
- This step ensures that your content in the Document Authoring environment (da.live) is properly linked to your site repository.
- Screenshot:
Step 4: Link Repository to Data
Next, connect your repository to data sources (e.g., commerce backend or environment configuration).
- Locate demo-config.json in your project.
- Rename it to config.json.
- Update the values with your environment-specific details such as API endpoints, project name, and organization identifiers.
- Screenshot:
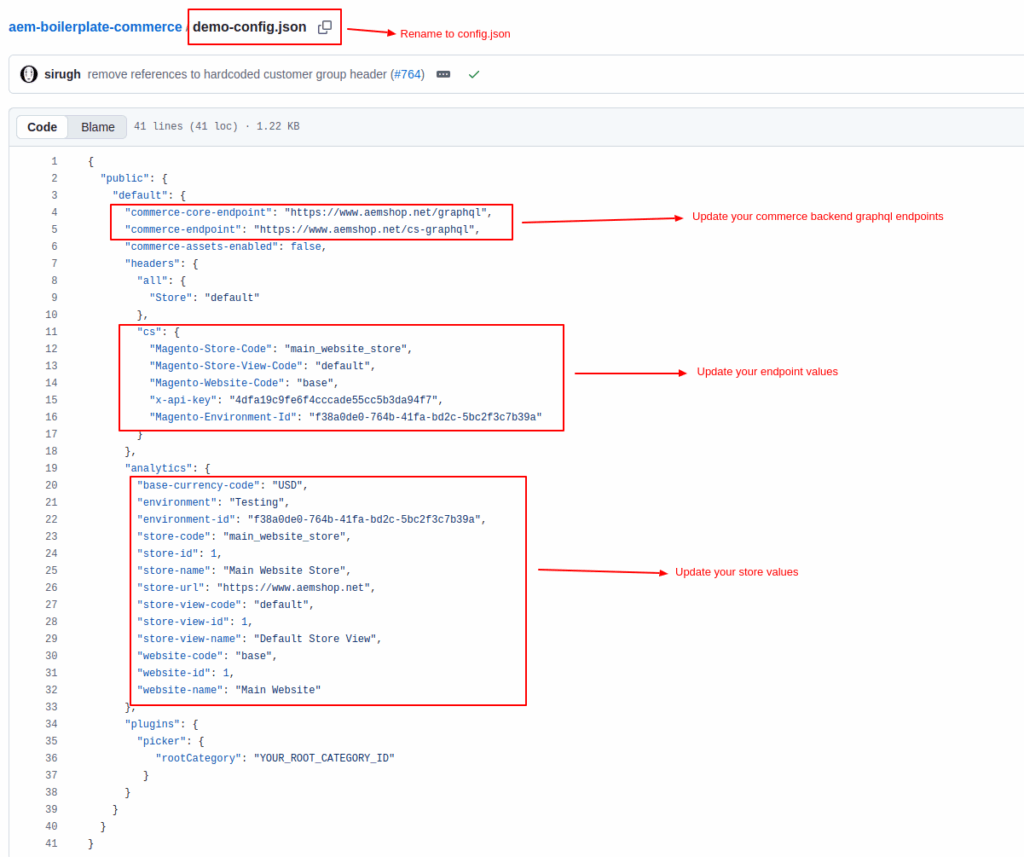
This configuration allows your storefront to fetch live data (e.g., products, prices, or catalog information) directly from Adobe Commerce or other backend services.
Step 5: Add Content in the Document Authoring Environment
Once your repo is configured, set up the authoring environment using Site Creator hosted at https://da.live/:
- Open the Site Creator tool: Storefront Site Creator
- You’ll see two setup options:
- Create new site (code and content):
Select this if you want to create both the code base and the authoring environment directly from Site Creator. This is useful when starting from scratch without a pre-existing GitHub repository.
- Use existing code repo (content only):
Choose this if you’ve already created your code repository from the boilerplate (as we did in the previous steps).
- In our case, since the code repository is already set up, we’ll select this second option.
- Choose your GitHub repository and organization from the dropdown.
- Create and link your content project.
- Screenshot:
This will set up your Document Author environment, where content authors can use Google Docs or Microsoft Word to create and publish pages directly to the live preview.
Step 6: Save and Manage Project Links
After setup, the Site Creator tool will display three important URLs:
- Code Repository: Your GitHub link for managing code.
- Content Authoring Environment: The da.live link for document-based authoring.
- Live Preview URL: Your .aem.page preview domain where you can test updates before production.
- Screenshot:
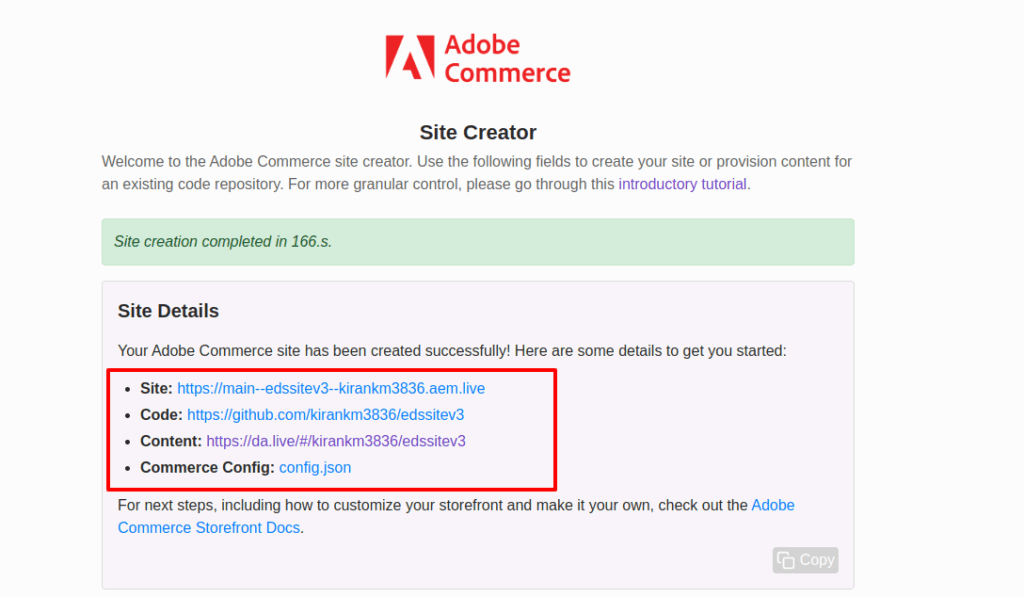
Be sure to save these URLs, they’ll be used regularly by both developers and content authors.
Reference – Adobe Experience League – Create Storefront Guide
Conclusion
Adobe Edge Delivery Services (EDS) is the next step in how websites deliver content — combining speed, simplicity, and scalability. With EDS, teams can easily create and publish content using familiar tools like Google Docs or Microsoft Word, while the system delivers that content instantly through Adobe’s powerful edge network. This means faster, more reliable, and SEO-friendly websites without complex setup or maintenance.
For businesses looking to upgrade their Adobe Experience Cloud, working with an enterprise ecommerce solution partner like Klizer helps ensure smooth implementation, quicker launches, and top-notch website performance.








